Your Hearing Health
Recognise the signs of hearing loss and how they impact your life.
About Hearing Loss
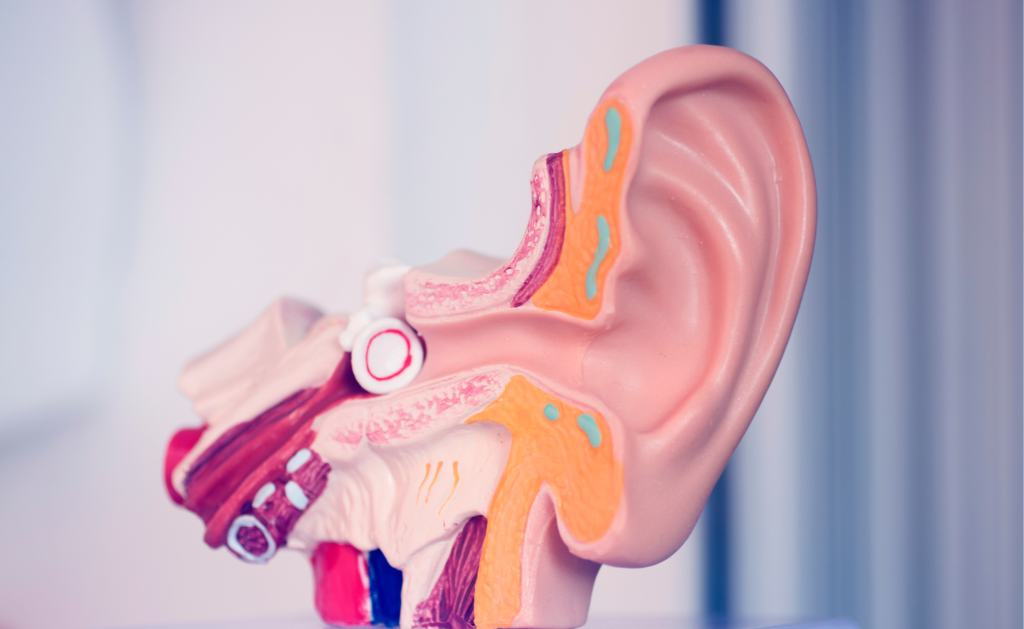
At ONDC Hearing Specialists, we can evaluate your hearing and offer guidance on how to address any hearing loss detected.
Hearing is a fascinating process that begins when sound waves enter our ears. The outer ear catches these waves and funnels them into the ear canal, causing the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted to three tiny bones in the middle ear, amplifying the sound. The stapes bone, in particular, passes the vibrations into the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear. Inside the cochlea, hair cells convert the mechanical energy into electrical signals, which are then sent through the auditory nerve to the brain. The brain interprets these signals, allowing us to perceive and understand the sounds around us.
When parts of the ear or auditory pathway don’t function properly, it can result in hearing loss. This can make communication challenging, frustrating and significantly impact a person and their loved ones’ lives.
Signs of hearing loss in adults you or a loved one may experience
- Difficulty hearing in background noise
- Turning the TV or radio louder than others
- Asking people to repeat; saying ‘what’ often
- Difficulty understanding women’s and children’s voice
- When people are speaking feeling like they sound muffled
- Difficulty understanding people unless they are facing you
- Constant noise or ringing in the ears
- Speech is delayed or unclear compared to other children their age
- Appears inattentive, restless or expresses some behavioural problems.
- Likes the TV or music played louder than usual or louder than others
- Pulling at their ears or complaining their ears are ‘sore’
- There are frequent requests for you to repeat things or perhaps they say ‘What?’ regularly
- Not turning their head to sound or not being started by loud noises
There are various types of hearing loss, each requiring different approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and care. The three main categories of hearing loss include conductive, sensorineural, and mixed.
Problems in the outer or middle ear can lead to Conductive Hearing Loss, where the sound signal is obstructed from reaching the inner ear.
Fluid in the middle ear (ear infection), a perforated eardrum, wax build-up, or damage to the tiny bones in the middle ear (ossicles) are the usual culprits of conductive hearing loss.
This type of hearing issue is typically temporary and can usually be addressed with medical treatment. However, if medical treatment is not suitable or effective, hearing aids could be a viable alternative for treatment.
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common form of hearing impairment. It can be caused by a variety of factors such as aging, exposure to loud noises, injury, illness, specific medications, or a genetic predisposition. Generally, the main causes behind sensorineural hearing loss are age and exposure to loud noises.
This kind of hearing loss is typically not treated by medical or surgical intervention; the recommended course of action for most cases is the use of hearing aids. Individuals with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss may also want to explore the option of cochlear implants.
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss may occur very suddenly or over a few days. It is important to see an Ears’ Nose & Throat Doctor (ENT) or contact our clinic for assistance as soon as possible.
Mixed hearing loss happens when someone experiences both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. For instance, someone who has been exposed to loud noises at work for a long time may also develop an ear infection. In some cases, the conductive part of the hearing loss can be treated medically, while hearing aids may be needed for the sensorineural part.
Depending on the cause of your hearing loss, treatment might involve removing ear wax, referring you for medical management of your hearing loss, or putting a rehabilitation program into place that might include counseling, communication skills and/or hearing aids.
It is important that if you ever notice a sudden change in your hearing, you should contact us or your doctor urgently.
Dizziness & Balance Problems

Our clinic is one of the few that is equipped with specialised vestibular equipment to help our university-qualified audiologists assess your vestibular system.
If you’re feeling dizzy, unsteady, or have any of the above symptoms and feel like you could be suffering from a balance disorder, it’s a good idea to consult with your GP or an Ear, Nose and Throat Specialist and obtain a referral for further evaluation.
Our ears are not just for hearing – they play a crucial role in our sense of balance. The brain also plays a vital role in maintaining balance, relying heavily on signals from the ears and eyes. Any disruptions in these areas can lead to balance issues. We understand the impact this condition can have on your daily life. Dealing with dizziness, lack of balance, and other symptoms can make simple tasks incredibly difficult, greatly affecting your overall well-being.
What are the symptoms of a dizziness or balance disturbance?
- Giddiness
- Vertigo (Spinning or moving sensation in the head)
- Imbalance/ loss of balance
- Lightheadedness
- Feeling unsteady
- Headaches
- Visual Symptoms
- Neck Symptoms
- Ear symptoms
Tinnitus
Can Tinnitus be treated?
While there is no cure for tinnitus, contact us at ONDC to schedule an appointment with one of our audiologists who will assess your hearing, provide insights on your tinnitus, and create a personalised management strategy. Your GP or ENT specialist may also recommend our services via referral.
Tinnitus treatment typically encompasses a variety of methods such as hearing aids, masking devices, self-management options and various sound therapy techniques.
Speak to our experienced audiology team today
Ringing sound in your ears?
Tinnitus could be calling
Commonly known as ear ringing, Tinnitus is a hearing issue where individuals perceive sounds like buzzing, hissing, or humming that are not externally audible in the real world. It can vary in intensity, frequency, and location, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds.
In Australia, around one in three individuals have encountered tinnitus at some stage, with approximately one in six enduring persistent symptoms.
Causes of Tinnitus
A frequent trigger for tinnitus is exposure to loud sounds. When the sensitive cells in the ear suffer damage from excessive noise, they may become overly stimulated and generate sounds that aren’t actually there. This can result in sensations of ringing, buzzing, or whistling in the ears.
Another potential factor contributing to tinnitus is the accumulation of earwax. Known as cerumen, earwax is a natural substance that the body produces to safeguard the ear and keep foreign particles out of the ear canal. However, when earwax builds up excessively or becomes impacted, it can obstruct the ear canal and lead to tinnitus.
In certain instances, tinnitus might indicate an underlying health issue.
